As the push for electric vehicles persists despite public reluctance, the once-promising solution for environmental concerns is revealing significant drawbacks. Issues like inadequate charging infrastructure, limited range, battery problems, high repair costs, and supply chain disruptions have plagued the industry.
Despite these challenges, proponents like Joe Biden continue to advocate for electric vehicles. However, the lack of consumer interest has led to substantial financial losses for manufacturers. Ford Motor Company, for instance, reported a staggering $4.7 billion loss in 2023 from its electric vehicle product line, exceeding earlier projections.
The company attributed the losses primarily to intense competition driving down prices. With Ford selling around 72,608 electric vehicles in the year, the losses translate to roughly $65,000 per vehicle sold, an unsustainable business model. Moreover, Ford anticipates further losses, projecting up to $5.5 billion for 2024, particularly concerning in an election year.
Despite Chief Financial Officer John Lawler’s optimistic remarks about future profitability and customer adoption, the reality suggests otherwise. Ford’s flagship electric vehicle, the F-150 Lightning pickup, saw diminished demand, leading to production cuts. This setback is notable, especially as Biden’s administration aimed for 50% of new vehicle sales to be electric by 2030.
Watch Biden test drive the Ford Lightning pickup here:
General Motors has also dialed back production and tempered expectations, posting a $1.7 billion loss on electric vehicles in just the fourth quarter of 2023. Ford went on to state: “We said yesterday that we will launch our second-generation EVs when they can be profitable and deliver the kind of returns we want, and we will build a stand-alone profitable EV business. Meantime, we’re improving the contribution margin of our first-generation EVs.”
A famous star was hospitalized.
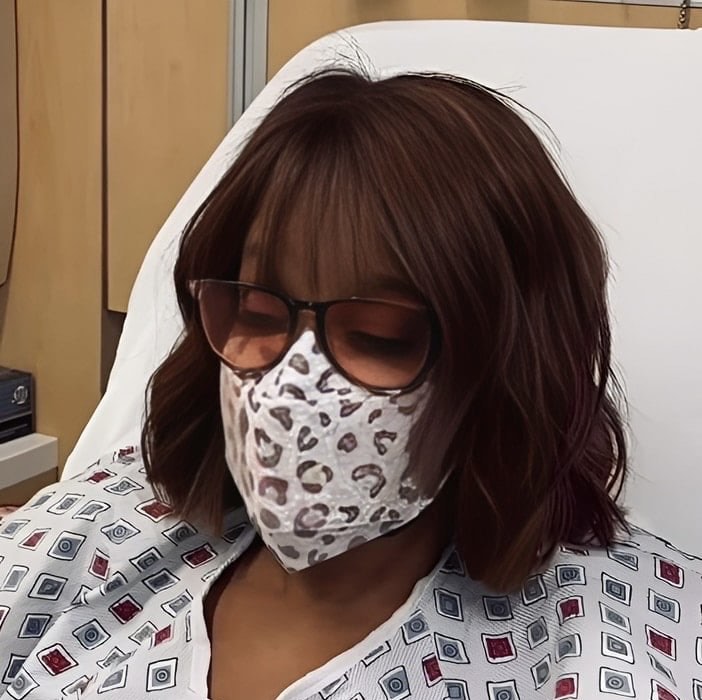
A representative for Oprah Winfrey just revealed on Instagram that the author will be making an appearance on CBS Mornings to discuss her most recent book recommendation.Sadly, over the weekend, the well-liked host contracted a stomach virus.Gayle King assumed command and gave the reason behind Winfrey’s absence.A spokesman for Winfrey told CNN in a statement on Tuesday that “Ms. Winfrey is recovering from a stomach virus and was given an IV due to dehydration at the recommendation of her doctor.”
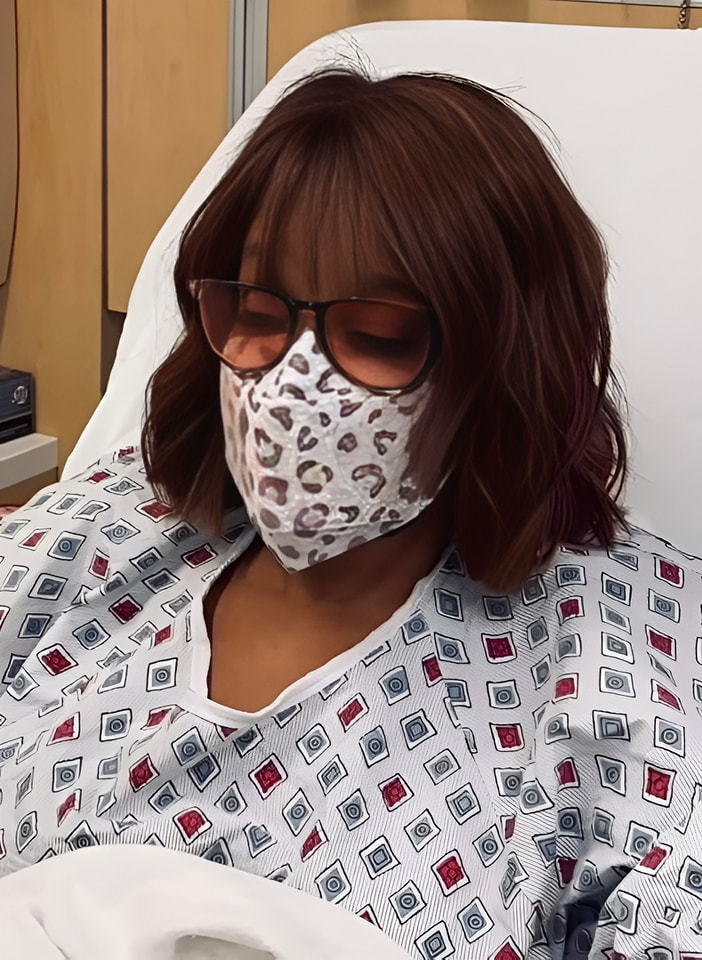
“She is getting more rest and improving every day.”Winfrey admitted to her best friend and journalist that she “couldn’t keep enough water down to stay hydrated” in a video chat that was shared on Gayle King’s Instagram page. This ultimately caused Winfrey to visit the hospital.King assured viewers that despite the health setback, Winfrey will eventually “be OK.”

She said, “I hope sharing that detail doesn’t bother her.”During a joint interview with the New York Times in January, Winfrey and King expressed their deep relationship and gave one other high accolades.She tells the truth with brutality. Even if it’s not what you want to hear,” King once observed in reference to Winfrey.

“[We] really, really enjoy each other.”In January of last year, Winfrey demonstrated that, at seventy, she is still in excellent physical shape.The media titan was seen running on the beach with her dog and another woman in the footage that she shared on Instagram.She thanked everyone who had sent her birthday greetings in the caption, praising health as the greatest gift.



Leave a Reply