A call that left Brittany Faske, a volunteer with the rescue organisation ADORE (All Dogs Official Rescue Enterprise of Houston), anxious came in January. A construction worker in Houston, Texas, noticed an injured Pit Bull with half of its face missing. According to the man, the dog hid in the bush and refused to allow anyone approach too close.
The woman was taken aback by the call and rushed to the spot. When she discovered the dog beside a ditch among the bags of food leftovers and old tyres, she realised he was in far worse condition than she had anticipated. The dog was in such horrible shape that she thought the best she could do was relieve his agony.
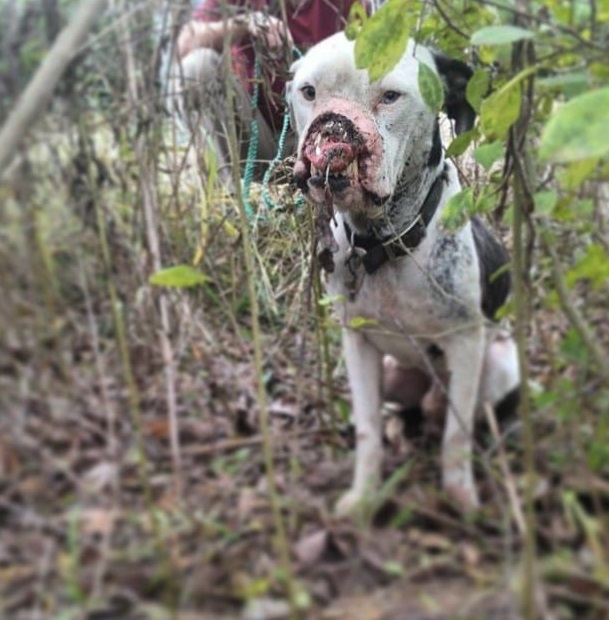

“This once-beautiful, big, and strong dog had been reduced to almost nothing.” He was so skinny that his ribs, hip bones, and backbone were clearly visible beneath his skin, in addition to his injuries. “He was covered in dirt and very weak,” Brittany explained to The Dodo.
The dog made a warning growl as she approached, but it didn’t startle her. She didn’t expect a different reaction from him, given the situation he was in and everything he had to go through and suffer through to remain that way.
After a while, the dog let Brittany to approach close enough to examine her injuries. The animal’s nose and snout were missing, and what was left hung in front of her face.
Brittany instantly realised it couldn’t have been an accident because the cut was so straight it could only have been made with a sharp instrument. So, that dog scenario was most likely the act of a human being, possibly the same one who left him lying there. In addition to the horrific sight of the wounds, the dog reeked of infection.
Brittany took Apollo, the dog she named, to the veterinarian after gaining his trust. Despite appearing to be in excruciating pain, the dog managed to relax and even fall asleep in the woman’s car. However, he was not yet fully safe.
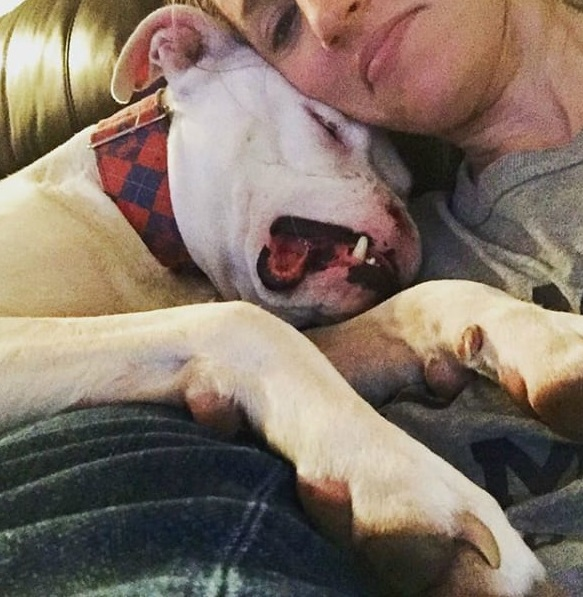

The dog required immediate medical attention, and Brittany was unsure if he could handle the therapies that were to follow. However, when Apollo arrived at the clinic, he trotted around the waiting area, sniffing people and interacting with the other dogs.
Apollo had heartworm, a disorder that arises when parasitic worms move through a dog’s tissues to its heart and can lead to death if left untreated, in addition to his facial injuries.
Brittany and the vet placed food and water in front of Apollo to determine his quality of life and ability to eat properly. He could have a shot if he can do it.
Apollo ate two bowls of food and water without hesitation. Then Apollo approached the woman who had saved him and rested his head on her leg. “From that moment on, we knew he wasn’t just any dog,” Brittany explained.
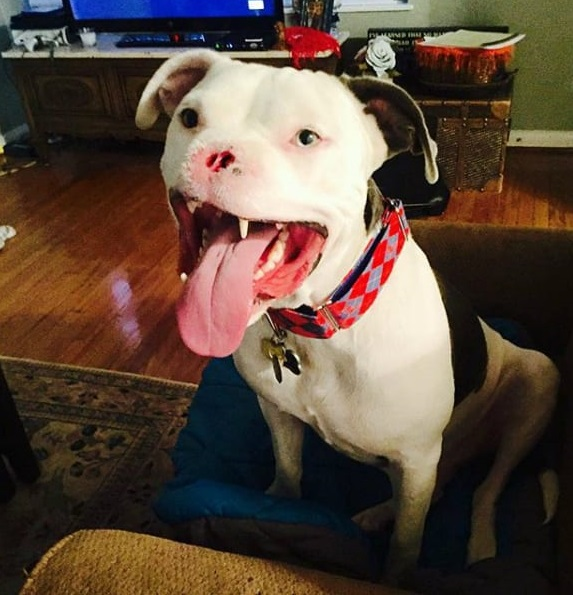

Apollo eventually underwent reconstructive surgery. The dog’s exterior nose had been removed, but he still had a nasal cavity through which he could breathe. During the procedure, the veterinarian wrapped a skin graft around the exposed bone in Apollo’s nasal cavity to protect what was left of his nose. While the vet had to remove part of the dog’s top jaw and some teeth, he was still able to maintain enough of his mouth for him to eat and drink regularly.
Meanwhile, Brittany had not considered adopting the dog; she was simply concerned with the surgery and the dog’s recovery. She knew, though, that she and Apollo had formed a special link that was growing stronger by the day.
Brittany introduced Apollo to her other dogs, two males over the age of ten. “They were powerful breeds with volatile temperaments.” Two old men who are grumpy. I wasn’t sure if they could take another dog. “They were used to being just the two of them and were very protective of me,” she explained.
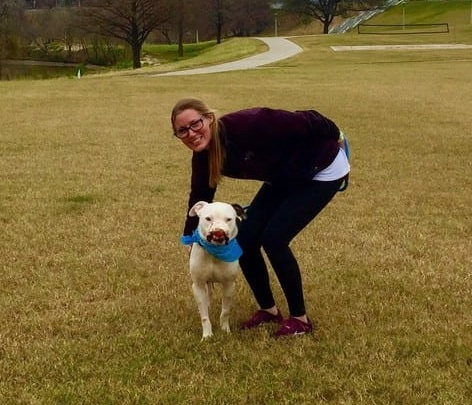

Once again, Apollo outperformed Brittany’s expectations. Apollo not only accepted the new dog, but he also adored the elder dogs. Another surprise element about Apollo was that he enjoyed being among others, which was unexpected given what he had been through. After that, Brittany made the obvious decision to officially adopt Apollo.
Apollo now lives a full life despite his facial injuries. His repaired nose functioned like any other dog’s nose, allowing him to breathe, smell, and sneeze normally. His reconstructed jaw does not prevent him from eating or playing.
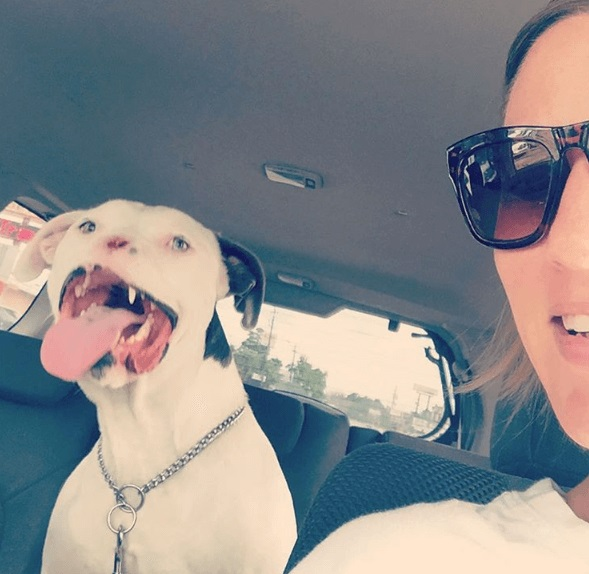

Apollo enjoys cuddling up in the recliner with Brittany and watching TV, playing with his dog brothers, eating, and sunbathing. Furthermore, the dog received personalised training sessions at a Total Control K9 College K9 course, where he attends classes every Saturday and appears to like it.
Apollo was able to overcome his emotional traumas thanks to Brittany’s devotion, which also made him a very caring and affectionate dog. “I’ve never met a happier dog.” “You can see their trust and love in their eyes,” Brittany says.
15 Facts About “Harry Potter” That Even the Most Avid Fans Have Probably Missed
The world of Harry Potter is one of the most beloved franchises across several generations. The seven books covering the captivating story of young wizards, in total, sold more than 450 million copies, and the movies grossed more than $7 billion. A part of such great success has been the detailed work of all people involved which we, as fans, can admire infinitely.
We at Now I’ve Seen Everything wanted to dive deep into this magical universe and brought you our curious finds.
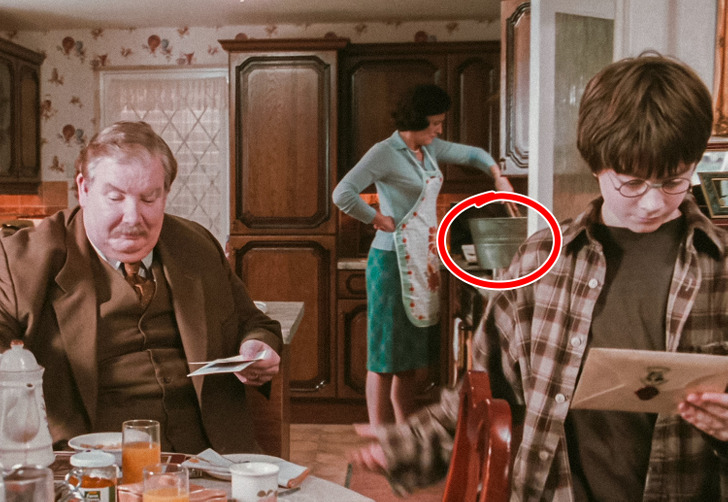
1. One might think that Aunt Petunia is cooking in this scene. But she is actually dyeing Dudley’s old clothes grey for Harry’s uniform. This is only ever mentioned in the first book.

2. Number 7 on Harry’s Quidditch uniform
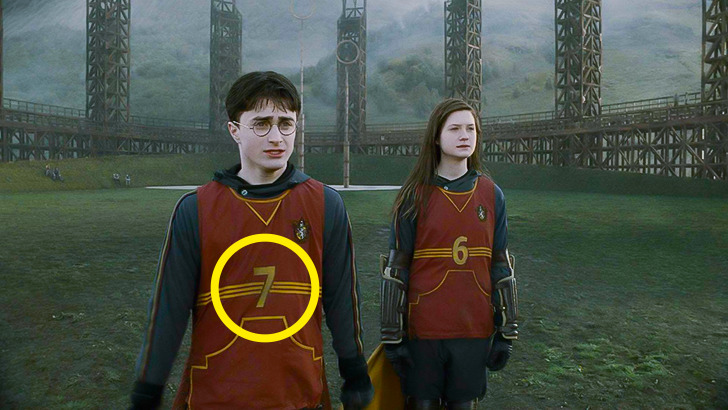

- Actually, the number 7 is a symbolic number in the world of JK Rowling. Moreover, Lord Voldemort has 7 Horcruxes and the last one, as we know, was Harry, which is quite symbolic too. However, the costume designer noted that the choice of this number for the Quidditch uniform is a reference to David Beckham, who played under this number a while back.
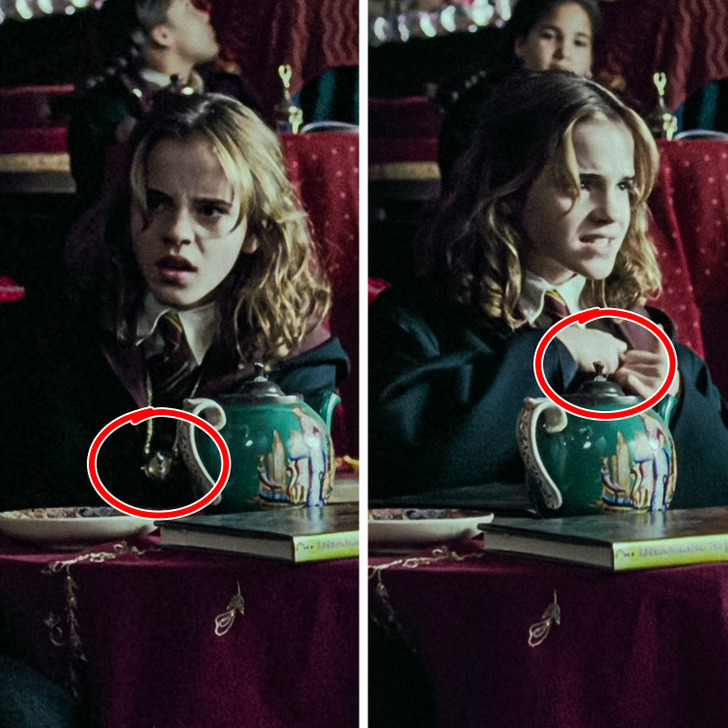
3. In the third movie, when Hermione appeared in class out of nowhere, we can actually see her time turner around her neck, which she hides in the next shot.

4. The scarves of Hermione, Ron, and Harry
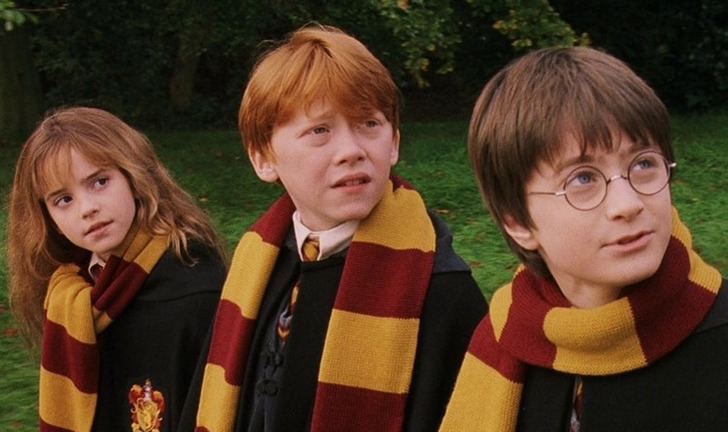

- The costume designers decided to hint at the character of each person with the help of tiny detail — a scarf. If you’re paying attention, you know that each character ties it in their own way. Hermione tightens it as neatly as possible, according to the rules. Harry throws the end of the scarf over his shoulder. Ron doesn’t tie this accessory at all.
5. Although it may have gone unnoticed amidst all the chaos, in Harry Potter and the Deathly Hallows: Part 1 we get to see a reunion between Hermione and Viktor Krum.

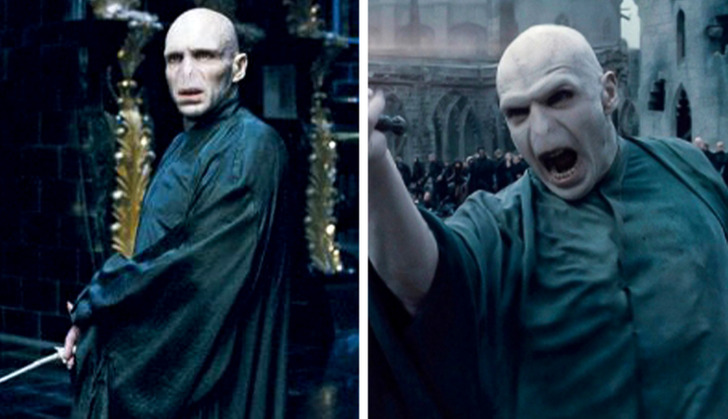
6. As the story progresses and Harry and his friends begin to destroy the Horcruxes, you can see how Voldemort’s clothes become discolored, his eyes droop, and small lesions appear on his skin as a sign that he is getting weaker.

7. The changing costumes of Dolores Umbridge

- In the image of Dolores, it was important to outline that she has power. We see that she, like many other powerful people, is rather conservative. For example, she wears the same hairdo and sticks to the same colors. Umbridge adores the color pink but its hues change as the plot develops.
- The costume designer commented on it in the following way, “I started with a lighter pink, and then as the film developed the pinks get hotter and hotter and hotter because she’s getting more and more hysterical.”
8. Harry’s scar
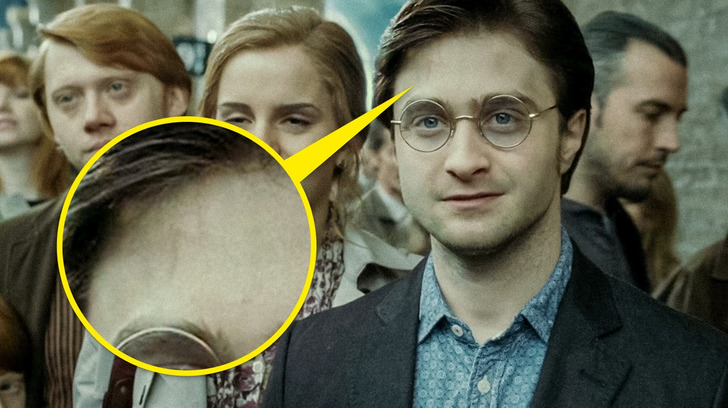
In the final shot of the film, Harry’s scar is noticeably faded and barely visible. It’s the reference to the last line of the novel series, “The scar had not pained Harry for 19 years. All was well.”
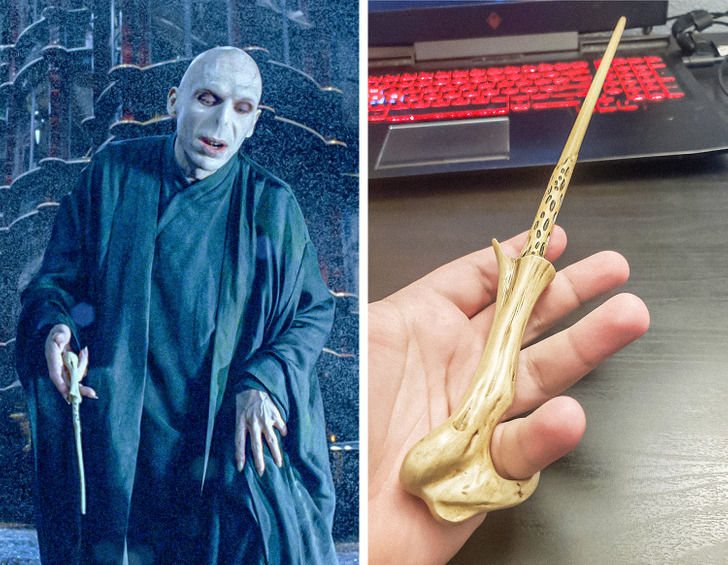
9. Ralph Fiennes (Lord Voldemort) asked for a hook to be added to Voldemort’s wand so that he could move more fluidly and “snake-like” without the wand falling from his hand.

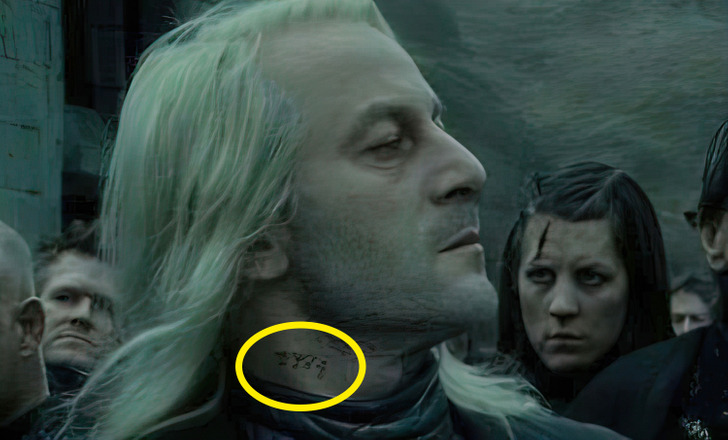
10. In the last movie, Lucius Malfoy is seen sporting a new tattoo on his neck. This is the prisoner number he was given when he entered Azkaban.

11. Gilderoy Lockhart’s wig
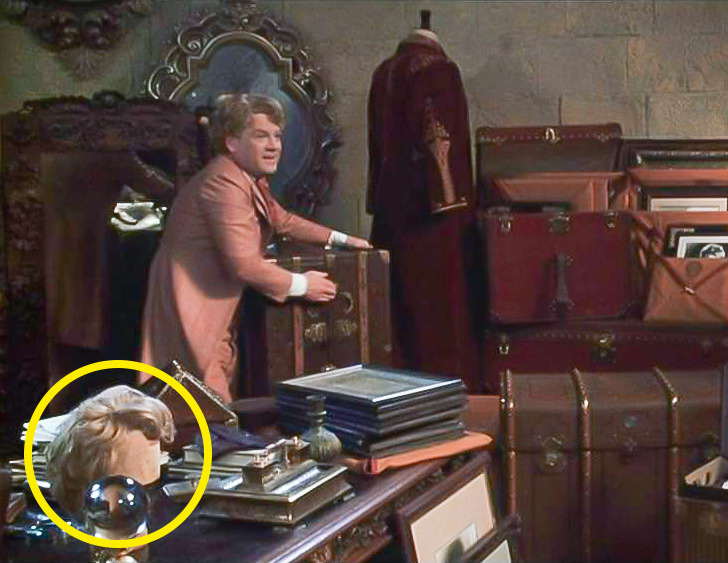

- In Harry Potter and the Chamber of Secrets, attentive viewers can notice that the professor of Defence against the Dark Arts, has a wig lying on his table. As we will later learn, Lockhart is a liar, who was cheating everyone and hadn’t done any feats. That is, he lies about everything and even his golden curls are fake.
12. Professor McGonagall has a secret talent.

- The Quidditch trophy from Harry Potter and the Sorcerers’ Stone not only features James Potter, Harry’s father but Professor McGonagall as well. Who would have guessed she was such a great player.
13. Hermione’s valuables.

- When Lockhart unleashes the pixies, Hermione immediately throws her books to the ground while no one else does because she knows the pixies will rip anything in plain sight apart.
14. Severus Snape and Gryffindor’s scarf
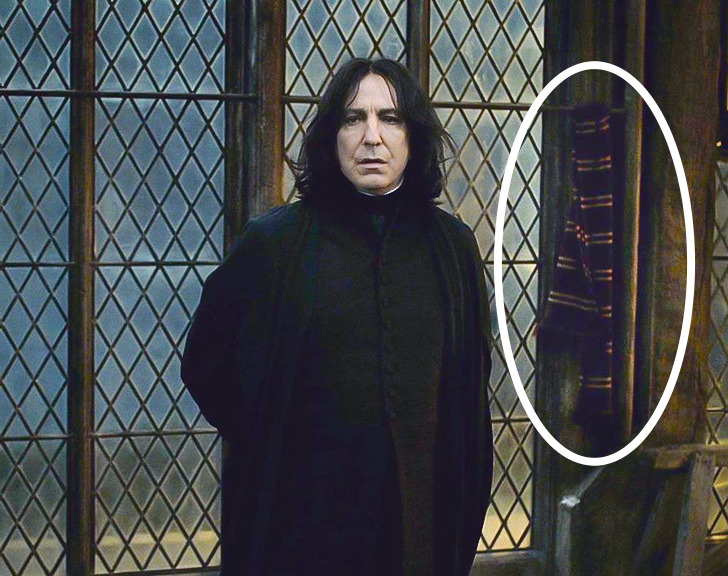

- Severus Snape is one of the most controversial characters. It’s not without reason that we see a striped scarf from Gryffindor hanging on the wall in the scene where he is killed. Perhaps he personifies the true inclination of Severus, and in due time he should have gone to Gryffindor, not to Slytherin.
- In the book, Dumbledore once says the following phrase relating to the distribution of students by faculty, “Sometimes I believe we sort too soon.” Perhaps, the professor was right. Perhaps, the scarf hanging in the closet is saying that people can change for the better.
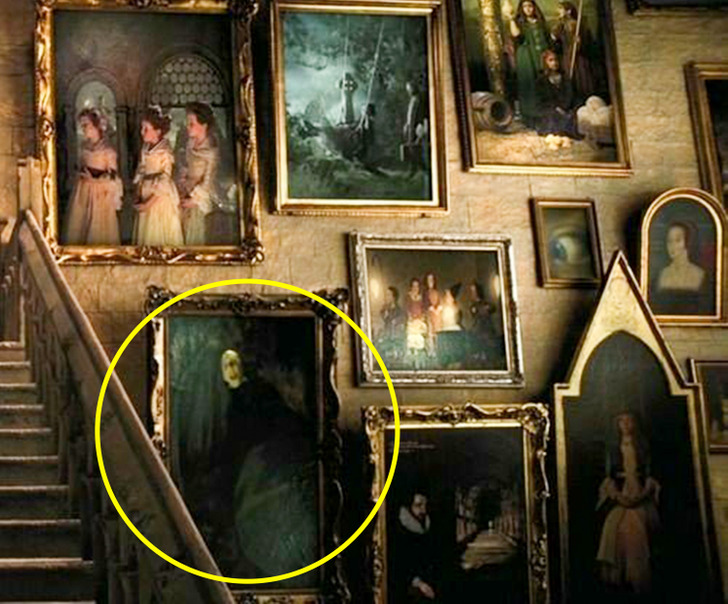
15. As strange as it may seem, in Harry Potter and the Prisoner of Azkaban, a portrait of Voldemort can be seen on the side of the staircase.

What details in Harry Potter did you manage to notice only after re-watching or re-reading each one?
Preview photo credit Harry Potter and the Chamber of Secrets / Warner Bros. Pictures, Harry Potter and the Deathly Hallows: Part 1 / Warner Bros. Pictures



 It’s totally understandable to feel let down if you don’t receive the birthday wishes you were hoping for. Maybe your friends
It’s totally understandable to feel let down if you don’t receive the birthday wishes you were hoping for. Maybe your friends 
Leave a Reply