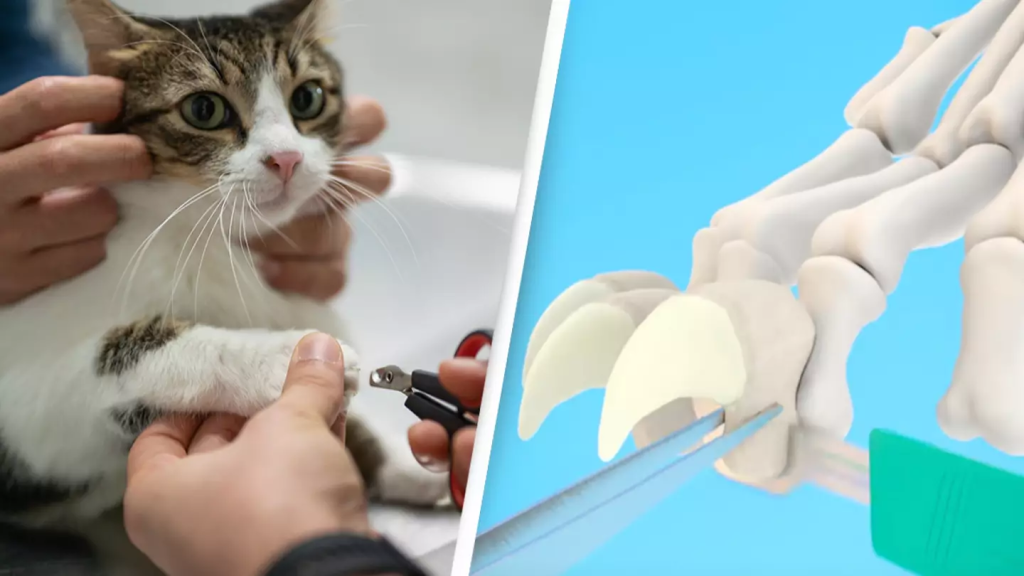
Certainly, declawing your cats is not a good idea.
A lot of people are just discovering on the internet why declawing cats is never a good idea.
The struggle will be familiar to the pet owners. Yes, the cat will sharpen its claws on the new couch you bought for the living room.
You can see why many cat owners choose to declaw their pet by considering the same reasoning that applies to any type of furniture in the house.
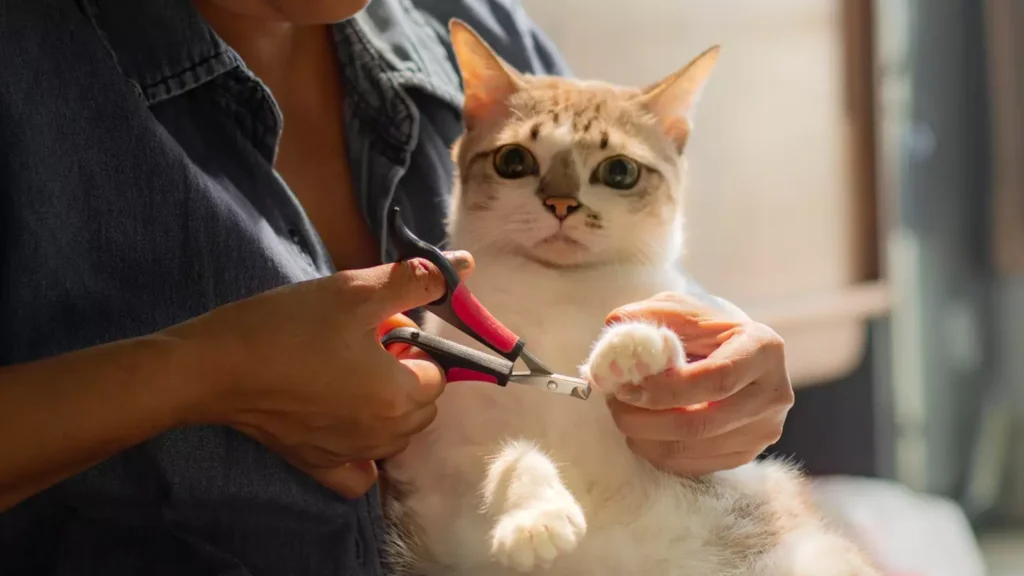

Even though it could be better for your couch, that might not be the best thing for your cat.
Declawing is defined as “the amputation of the last bone of each toe on a cat’s paw” by The Humane Society of the United States, and that definition alone should dissuade you from engaging in the procedure.
Our animal buddies endure great anguish during declawing, as the society compared it to chopping off your finger at the last knuckle.
They continued, giving an explanation: “Using a scalpel or guillotine clipper, amputation is the usual way of declawing. The feet are wrapped, and the incisions are sealed with surgical glue or stitches.”
Recently, the declawing debate has spread to Twitter, largely due to the popular account “non aesthetic things.”
The user wrote, “This is why you shouldn’t declaw your cat,” and included a video that showed what happens to cats who are declawed.
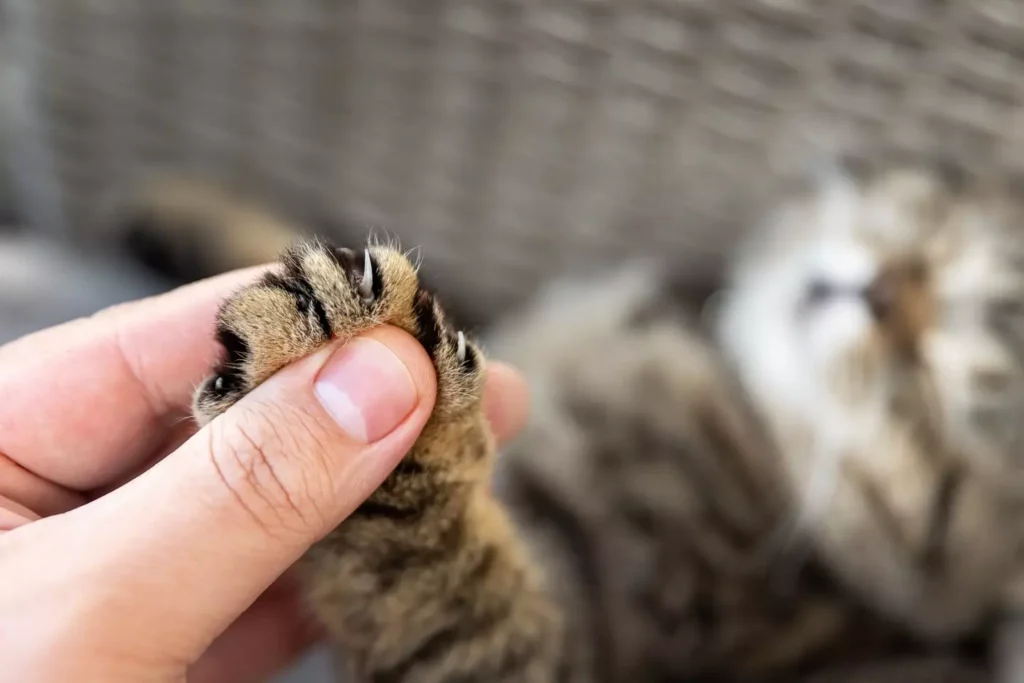

Basically, declawing causes the last bone on a cat’s toes to be severed and removed. This impacts the tendons and ligaments and eliminates the claw entirely.
Cats may feel “extreme pain” when they learn to walk on what are essentially amputated toes, but they do heal eventually.
The movie described how this causes cats to struggle with walking, jumping, and balance, which would ultimately cause them to exhaust their nine lives.
Even in the long run, defewing can have negative effects like arthritis, persistent pain, and limited mobility.

Oh, poor infants.
Many people have flocked to the Twitter video’s comments section, where many have only recently discovered the grim reality of declawing.
One member said, “So declawing your cat is just removing parts of their feet wth.”
One person wrote, “literally, take off our very last finger bone that we literally use to type,” another wrote, “It’s absurd to think that a significant portion of people in the US declaw their cats.” A third person wrote, ” To be honest, I’ve never heard of this outside of the United States.”
Four people said, “Declawing should be banned everywhere, it’s just inhumane!” in the meantime.
Sad news about Brad Pitt. The announcement was made by the great actor himself:
Actor Brad Pitt revealed in a recent interview that he suffers from prosopagnosia, a rare neurological disorder also known as “facial blindness.”
Dani Blum describes the disorder’s signs, causes, and remedies in an article for the New York Times.
Borna Bonakdarpour, a behavioral neurologist at Northwestern Medicine, claims that face blindness—not color blindness or general vision impairment—is the main symptom of prosopagnosia.

The National Institute of Neurological Disorders and Stroke states that there is no connection between the illness and memory loss, vision problems, or learning impairments.
Blum continues, “It is not the same as forgetting or occasionally having trouble finding the correct word.
The severity of prosopagnosia will differ from person to person.
For instance, some people might have problems identifying a familiar face, such as that of a close friend or relative, while others might have trouble identifying their own reflection.
Additionally, some people might not be able to distinguish between faces and objects.
Notably, some data indicates that individuals with prosopagnosia may have chronic anxiety or depression due to the loneliness and fear that are frequently associated with the illness.
Blum notes that some people avoid contact with family members and other loved ones out of concern that they won’t be able to properly recognize or acknowledge them.
“Navigating basic social relationships with prosopagnosia can become difficult,” she says.
Pitt admitted that he has trouble recognizing people’s faces for years in a recent interview with GQ, despite never having gotten a formal prosopagnosia diagnosis.
In fact, Pitt claimed in a 2013 interview with Esquire that his difficulty recognizing people’s appearances was so great that it frequently made him want to isolate himself.
He explained, “That’s why I stay at home.
What is the condition’s cause?
People who are diagnosed with prosopagnosia often fall into one of two categories: either they are born with it or they acquire it.
However, estimations reveal that as many as one in every 50 people may struggle with some lifetime form of the disorder, and experts hypothesize that it may run in families.
According to Blum, research “suggests that congenital, or lifelong, prosopagnosia is less prevalent.”
According to Andrey Stojic, director of general neurology at the Cleveland Clinic, children born with the illness “don’t seem to have any visible structural abnormality” in the brain.
Notably, doctors don’t fully understand what causes congenital prosopagnosia because there aren’t any obvious brain lesions in persons who have it.
In contrast, people who develop prosopagnosia later in life may have brain abnormalities brought on by a trauma or head injury.
According to Bonakdarpour, individuals can also develop prosopagnosia while dealing with Alzheimer’s illness or following a stroke.
What therapies are available for prosopagnosia?
Prosopagnosia is now untreatable, according to Bonakdarpour. The problem can be treated, though.
People who have the syndrome frequently attempt to distinguish between people by focusing on physical characteristics like hair color, gait, or voice.


Leave a Reply